A Gentle Introduction to GPTs
Mlearning.ai
FEBRUARY 19, 2023
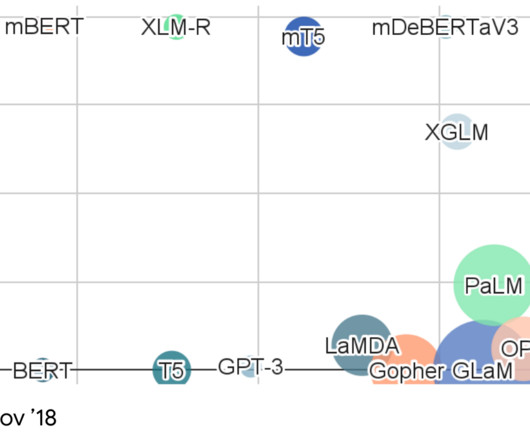
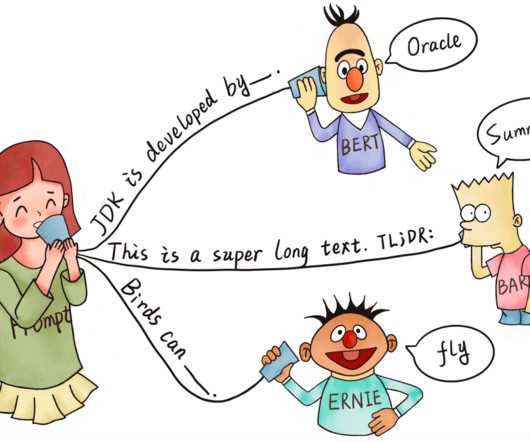
It combines techniques from computational linguistics, probabilistic modeling, deep learning to make computers intelligent enough to grasp the context and the intent of the language. GPT-3 is a successor to the earlier GPT-2 (released in Feb 2019) and GPT-1 (released in June 2018) models .










Let's personalize your content